Since it’s scheduled to be reviewed in 2025, there has been a series of discussions on the Animal Welfare and Management Act.
Together with Japan Anti-Vivisection Association (JAVA) and PEACE(Put an End to Animal Cruelty and Exploitation), the Animal Rights Center Japan compiled requests to further update the law.
As we demanded for the revision in 2019, situations for livestock animals have improved significantly, so we’re focusing on what is yet to be realized this time around. In addition, we request the law be properly followed since it has not been strictly enforced lately.
Transition to Animal Welfare(福祉)Act from Animal Protection(愛護)Act
1.Clarify animal welfare by changing to “the purpose of this Act is to establish ethical responsibilities to uphold animal welfare among citizens …”from the current“the purpose of this Act is to engender a spirit for animal welfare among citizens …” in the Article 1 of the law.
Reason: Incorporating Animal Welfare (in Japanese or Katakana) into the purpose of the Animal Welfare Act aims will enhance the well-being of the animals themselves.
Note: The current purpose of the Animal Welfare Act is translated into English as “to engender a spirit for animal welfare among citizens”. However, a direct translation from Japanese would be “cultivating an atmosphere of animal care among the citizens”, which does not include the word ‘welfare’.
2.Include five freedoms to the Fundamental Principle in Article 2. Namely, add“freedom from fear and distress”and“freedom to express natural behavior”to the three freedoms already stated in the current principle.
Reason: This will clearly indicate that psychological abuse or neglect is also illegal. The current principles don’t seem to include these two freedoms that are foundations of animal welfare stating the 5 freedoms.
Expansion of Animals and Businesses in Scope
1. Remove the limitation of animals and change to“all vertebrates” in Article 10 that stipulates business handling animals. [Supplementary Provisions]
2. Remove the limitation of animals and change to “all vertebrates” in Article 44, Clause 4 that specifies the term “protected animal.” [Supplementary Provisions]
Reason: We need to include all vertebrates to be in scope of the animals just like the neighboring countries, such as Taiwan, South Korea and the Philippines. Scientifically speaking, there is no reason to differentiate one from others among mammals, reptiles, birds, amphibians, and fish in light of animal protection.
3.Expand the business in scope in Article 10 to include any businesses handling vertebrates. Also include facilities conducting animal experiments, companies selling animals for experiments and live food, agriculture business, transportations, facility that handles assistance dogs, and video makers that handle animals. [Supplementary Provisions]
Reason: Despite being a business dealing with animals, the lack of applicability creates inequality. While different regulations may apply to livestock and other sectors, it is necessary to include all businesses handling animals, including those in the animal industry, under the regulation of animal welfare standards to ensure fairness.
4.Chagen to “all vertebrates” from just “dogs and cats”in Article 37 that define breeders.
Reason: Not limited to dogs and cats, there is a widespread occurrence of animal hoarding that leads to tragic situations.
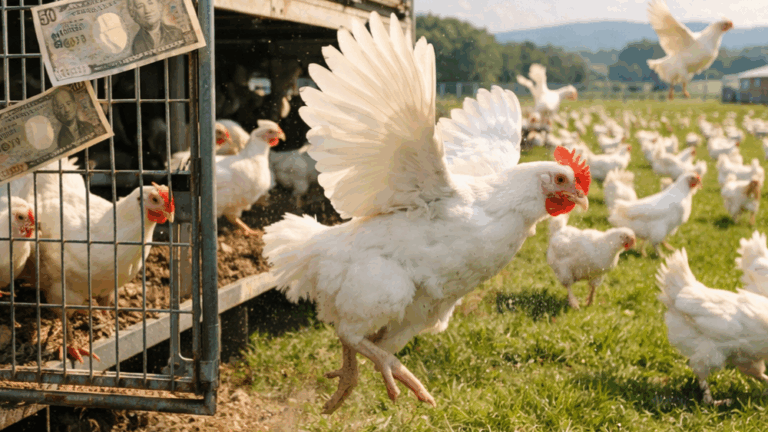
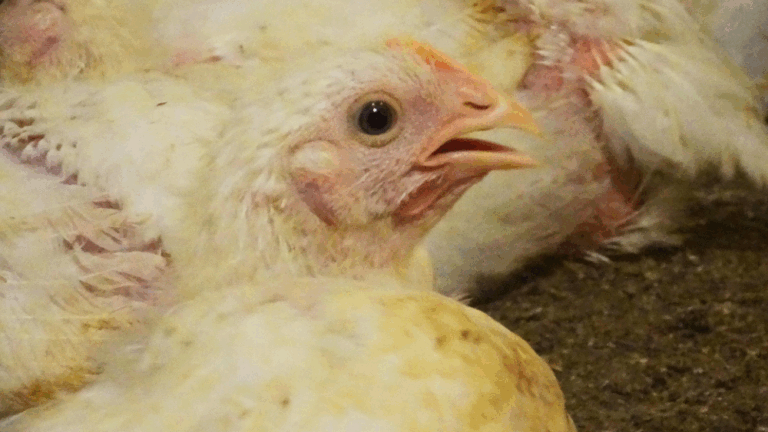
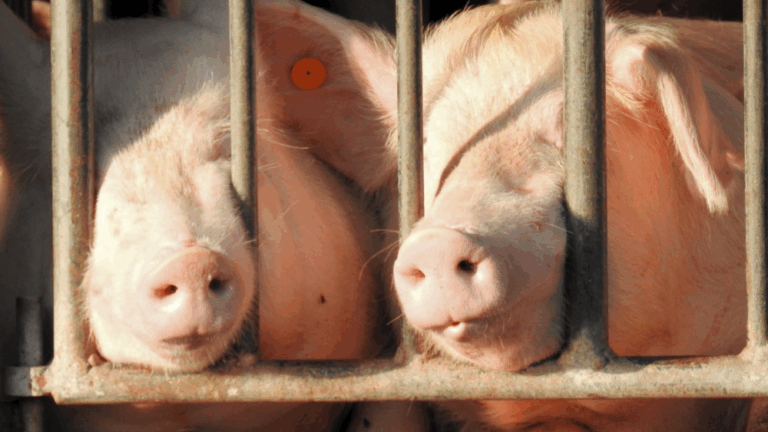
Addition of an Article to Cover Industry Animals
1.Add an article to cover the following clauses to better protect livestock animals. Apply penalties when 3), 4), and 5) are violated.
Reason: We must include such an article to meet global standards. Fines or other forms of penal provisions are essential in order to enforce the law.
①Oblige companies to transition into a new method to ensure the five freedoms for livestock animals.
Reason: As quite a few Japanese prominent companies in the food industry would agree, these five freedoms were originally suggested for livestock animals, which is now globally recognized as the gold standard in animal welfare.
②Closely observe new trends and pay attention to global standards.
Reason: Technology to ensure animal welfare for livestock animals has been rapidly changing. It’s crucial to observe the trends of global standards for animals, sustainability and economy.
③Implement a new process to ensure livestock animals are knocked unconscious before getting slaughtered. *May allow a 5- year transitional period.
Reason: Although this practice is already in place for most mammals, it doesn’t often apply to chickens or other birds. Internationally speaking, this is a requirement and slaughtering animals while being conscious is no longer accepted.
④Provide enough space for animals. At minimum, animals must be able to lay down without touching walls or other animals. *Implement this for when building new facilities. May allow a 2-year transitional period for existing buildings.
Reason: Animals tend to be confined in a tight space as there is not much land in Japan, which can cause breakout of diseases, proliferation of viruses or germs.
⑤As a requirement, use anesthesia or pain medications when surgeries are conducted.
*May allow a 3- year transitional period.
Reason: Globally, surgeries or operations for animals that cause excruciating pain have been phased out. When necessary, using anesthesia is understood as a more human method when neutering, tail docking, or dehorning.
2.Amend the Care and Keeping of Industrial Animals to follow the standards set by World orgnisation of Animal Health (WOAH, formerly known as OIE). These must be observance of obligations. [Resolutions/Basic Guidelines]
Reason: The standards set by WOAH are quite basic so these must be obliged. We must set specific standards for slaughtering while closely examining the animal welfare guidelines to handle animals by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF).
3.Include livestock animals facilities in the definition of animal handling businesses.
Reason: The MAFF or MHLW (Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare) must maintain records so they can instruct these businesses when needed.
Mandating Humane Alternatives to Animals Experiments. Ensuring 3Rs.
1.Make alternative methods to that of the use of animals in Article 41 (1)“Method to Be Applied, Subsequent Measures in the Case of Providing Animals for Scientific Use” mandatory. [Supplementary Provisions]
Reason: The ideas of Replace, Reduce, and Refine must be mandatory. Globally,“3Rs alternatives”for use of animals in science experiments are regarded as standards and avoiding animal experiments to minimize sufferings is widely acknowledged.
2.Make it mandatory when there is a clear alternative to animal experiments.
Reason: There are cases where animal experiments are conducted even when there’s clearly an alternate method. This is causing unnecessary suffering for animals.
3.Include development and dissemination of humane alternatives as our responsibility. [Supplementary Provisions]
Reason: The nation must invest in developing and disseminating humane alternatives to promote research that is globally competitive. To that end, such effort must be included as a responsibility in the Act.
4.Include animal experiment facilities in the definition of animal handling businesses.
Reason: We must include usage of humane alternatives and reduction of animal use in Standards for Caring For or Keeping Animals so registered facilities are obligated to follow the rules.
Addition of an Article about Transportation
1.Add an article to cover transportation for animals to include the following items:
Reason: It is not normal that there’s no article to cover this in the current Act since transportation is one of the most stressful aspects for animals.
①Minimize transport time for animals.
②Make efforts to reduce pain and stress.
③Hydrate animals during transportation. Feed if transport time exceeds 12 hours.
④Keep temperature, lighting, ventaration, and, humidity and flooring that is suitable for animals’ natural behaviors.
Reason: Transportation is so stressful for animals that can sometimes lead to death. We must make best efforts to minimize transport time to reduce stress. Though, it’s worth noting some vendors do not transport live animals, today’s distribution system takes into account that animals might die during transportation, which should be considered illegal. However, no article stipulates improvements for transportation.
2.Create other guidelines by following 7.2 Transport Animals by Sea, 7.3 Transport Animals by Land, 7.4 Transport Animals by Air in the Animal Welfare Standards by WOAH.
Reason: The guideline must follow the Animal Welfare Standards by WOAH other than those ① through ④. This will need to be mandatory.
3.Include the obligation clause to follow this Article about transportation for animal handling businesses.
Reason: Responsibilities for animal handling businesses must be clearly stated.
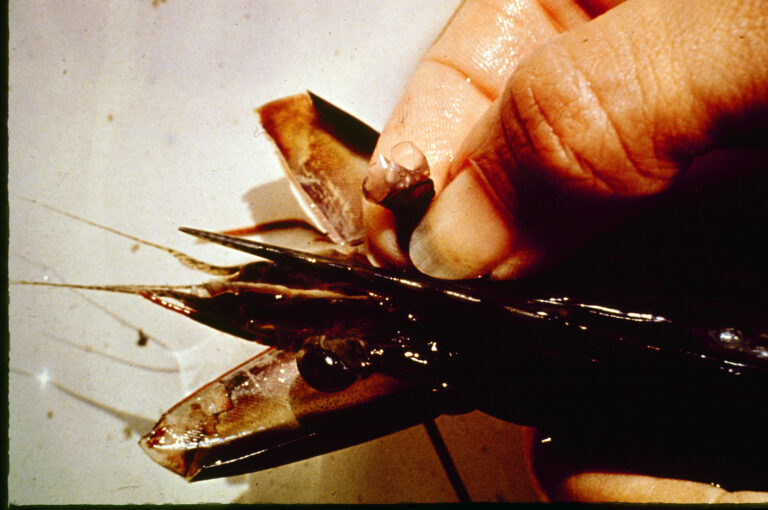
Improving methods of destroying animals
1.Amend Article 40 regarding destroying animals as follows:
Article 40: In the case where an animal must be destroyed, an animal must first be unconscious, then a method that is quick and minimizes the pain must be used.
Reason: According to global standards, it is essential to stun animals before proceeding with the slaughter process.
2.Upon the change mentioned above, prohibit local governments from culling mammals using carbon dioxide alone.[also mentioned in the Diet responses].
Reason: At one Environment Committee in the House of Councilors, there was a discussion that killing methods that cause pain for animals shall disappear in future. We already have a more humane method to slaughter chickens by using a mixture of carbon dioxide and argon.
For the slaughter of chickens, it is considered more humane to use methods involving a mixture of carbon dioxide and argon, as well as the gradual filling of gas. However, the use of carbon dioxide alone for the culling of mammals is inhumane and therefore needs to be abolished.
Clarifications on the Current Penal Provisions
1.Drop debilitation or death and prohibit cruelty itself in Article 44 (2).
Reason: The current Article (2) may not be enforced if cruelty does not cause debilitation or death. We must change the wording in this article to penalize animal cruelty itself.
2.Add the following ① through ⑮ in the definition of cruelty in Penal Provisions.
①Inflict unnecessary pain.
②Inflict physical pain.
③Overwork or subject to excessive labor.
④Restrain, confine in a small space, tether, or prevent proper movement.
⑤Transport in a manner causing distress or pain.
⑥Leave animals unattended in a vehicle in conditions that endanger their life or health
⑦Expose to inappropriate levels of brightness.
⑧Inflict mental pain, perpetuate stress.
⑨Practice husbandry management contrary to natural habits or behaviors.
⑩Practice husbandry management contrary to natural habits or behaviors.
⑪Neglect appropriate feeding and watering according to natural habits.
⑫Neglect health care, including treatment of injuries or prevention of diseases.
⑬Perform surgical procedures without a veterinary license.
⑭Force animals to fight.
⑮Expand the scope to include intentional and deliberate abuse, neglect, or acts that may be considered willful misconduct beyond those mentioned above.
Cases of abuse other than physical violence such as hitting and kicking may not be recognized as abuse by the police.
Therefore, there is a need to clarify the definition further by following the UK’s “Animal Welfare Act 2006” in which penalties are imposed for causing unnecessary pain. [Link: https://onl.sc/Dv3A4qa]
Protection of Abused Animals
1.Enable the emergency temporary protection of abused animals by the administration.
Reason: In the current situation where animals cannot be forcibly removed from the abuser or malicious owner, animals in emergency situations are left at risk without rescue. Moreover, in situations where animals are held hostage, the administration and police cannot take strong measures against abusers or malicious owners in the current Act.
2.Prevent those who have caused harm, abused, improperly cared for, or abandoned animals from keeping animals again.
Reason: To reduce the number of animals becoming victims and to lighten the efforts of the administration, police, and animal welfare organizations, individuals penalized under the Animal Welfare Act or those who received orders from the administration due to improper care should be prohibited from keeping animals again.
Enhancement of Regulation for Type 1 Animal Handling Businesses: ①Prohibition of mobile exhibitions and sales
We shall prohibit mobile exhibition or sales by imposing the following:
①Mandatory inspection during registration and renewal. [Resolutions]
②Prohibition of registration under event organizers’ names; mandatory registration for each operator.
③Prohibition of registration at locations other than fixed business addresses (prohibition of sales and exhibitions in event venues, parking lots, paAfter installation, impose a quarantine period of 2 weeks for animals to be handled.
⑤Automatic removal of registration if requirements are not met (e.g., loss of land and building rights)
Reason: Operation varies ambiguously across administrations. Some registrations are conducted under event organizers’ names, not reflecting the intent of the law. Also, cases are observed where facilities registered for 5 years are not operational entities except during events, presenting problems.
It is necessary to prohibit by strengthening the regulation of mobile exhibitions and sales. This follows the example of the UK’s ‘The Pet Animals Act 1951’, which prohibits the sale of animals as pets on roads, in public places, and in markets.
Enhancement of Regulation for Type 1 Animal Handling Businesses: ②Empowering local government officials as “Animal G-Men”
Establish a system for administrations to swiftly and accurately carry out procedures against abuse.
1.Mandate a mandatory inspection within one week, at the latest, after receiving a report of abuse. Make this mandatory under Article 24.
Reason: Some administrations do not respond are slow to respond to reports of abuse. It is necessary to mandate they respond within a specified period.
2.Upgrade the Ministry of the Environment’s guidelines to Regulations to better enforce. Inspect using a checklist format, and certify any instance as abuse if it matches any criterion.
Reason: In some cases, even if a case of abuse is observed, local governments and officials claim they’re not considered as abuse and fail to take appropriate action. It is undesirable for the judgment of abuse to vary among individuals. The introduction of a system that allows judgment based on common criteria is necessary.
3.When the administration discovers violations by Type 1 animal handlers or those who were Type 1 animal handlers, they must make recommendations, and orders must be issued for the necessary measures. This should be mandated in Articles 23 and 24-2.
①Amend the deadline for recommendations and orders to be within one month from three months; improvements must be made within one month for all issues.
②If all issues are not resolved, the administration must proceed to the next measures, such as ordering measures, administrative penalties, or indictment for animal abuse.
Reason: Guidance often do not lead to improvement, so recommendations and orders must be mandated to the administration. (Guidance is not explicitly defined in the law)
There is a case where one improvement is considered acceptable while other issues remain. Therefore, it is necessary to mandate the advancement of procedures if improvements are not made for all issues.
4.Obligate the cancellation of registration, etc., for violations of orders, etc., from “possible” to mandatory, ordering immediate registration cancellation, or ordering a suspension of business within three months under Article 19.
Reason: To ensure reduction of malicious operators, this provision needs to be mandated.
5.Mandate the public disclosure of the business name during administrative recommendations, penalties, orders, cancellations, and suspensions of business under Article 23, Paragraph 3. Currently, we can only disclose businesses who violated after recommendation.
Reason: It can serve as a deterrent to businesses. The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism has a “Internet site search for Negative Information” where citizens can learn about past administrative penalties.
6.Authorize the Ministry of the Environment to issue directives to local governments, under Articles 245-4 to 245-8 of the Local Autonomy Act, in cases where standards violations or similar offenses occur and recommendations or orders are neglected within a specified period.
Reason: A system is necessary for the government to properly instruct municipalities that exhibit neglect of duties (Example: Building Standards Act Article 17.)
7.Strengthen the requirements for animal welfare management officers in Article 37, Paragraph 3.
①The Ministry of the Environment must conduct annual training for animal welfare management officers, and attendance and passing exams must be mandatory.
②In the training, provide examples of reports of abuse and responses by local governments in multiple municipalities, and conduct training on judgment of abuse and appropriate responses.
③Facilitate discussions among local governments to identify issues and work toward improvement.
Reason: For the “Animal G-Men” system of local government officials to be implemented appropriately, effectively, and efficiently, strict mandates and regulations alone are insufficient. It is essential to improve the capabilities and quality of on-site animal welfare officers.
Strengthening Responsibilities and Prohibitions for All Animal Owners or Occupiers
1.Introduce a whitelist system for animals, specifying which animals may be kept. Prohibit keeping other animals not in this whitelist.
Reason: The keeping of non-domesticated, wild-derived animals is inappropriate and should be limited from the perspective of animal welfare. [Biodiversity National Strategy]
2. Obligate those who transfer animals to confirm that the recipients are capable of proper care [Resolution].
3. Expand the scope of “Duties of Animal Sellers” in Article 8 to include not only sellers but all those who transfer animals.
Reason: Some local governments, animal organizations, and individuals easily transfer animals without confirming whether the recipient lives in a suitable dwelling or can handle care and management. As a result, problems such as abandonment, abuse, slaughter, or animal hoarding occur.
Events where live animals like hamsters are given as gifts without proper explanations of their habits and care methods, leading to abandonment or excessive breeding, are also issues.
This provision is necessary to show that lotteries are inappropriate. There is a risk of culling when selling or giving animals to elderly individuals. Since the current law does not regulate this, additions are necessary.
Correction of Inappropriate Care
1.Mandate proper care in Article 7, which is the responsibility of animal owners or processors. Change the phrase to “must comply with the standards.”
Reason: Violations persist despite only basic matters being written in the care and storage standards. To ensure thorough guidance and definite improvement, compliance needs to be mandated.
2.Remove guidance and advice, and mandate recommendations and orders related to recommendations in Article 25.
Reason: Guidance often do not lead to improvement, so recommendations and orders must be mandated to the administration. ⇒ Apply the “Animal G-Men” system to this as well.
3.Establish uniform technical standards for prefectural governors and others regarding the conditions of facilities (heating, cooling, space for confinement, exercise, etc.) to improve the situation of municipal facilities [Resolution]
Reason: Some facilities place puppies and kittens in unheated areas in the middle of Winter, presenting poor conditions. Under these circumstances, it’s impossible to guide residents on proper pet care.
Since the confinement situation is different from that of ordinary households, uniform standards for municipal facilities need to be established, creating an environment comfortable for confined animals. This will lead to the health of confined animals and an increase in the number of adoptions.
Other Revisions
1.Remove the following exclusion from the Article 10
“such animals are limited to mammals, birds, and reptiles, and exclude those pertaining to livestock agriculture and those being cared for or kept in order to be provided for use in testing and research, use in manufacturing biological preparations, or for other uses specified by Cabinet Order; The provision currently states, “such animals are limited to mammals, birds, and reptiles, and exclude those pertaining to livestock agriculture and those being cared for or kept in order to be provided for use in testing and research, use in manufacturing biological preparations, or for other uses specified by Cabinet Order; The same applies from this section to Section Four.”As such, the exemption clause is applied from Sections 1 to 4.
Reason: The removal of this exclusion provision is essential for expanding the target animal species and industries. This exclusion provision extends to “Section 4, Measures pertaining to Preservation of the Living Environment,”which means that administrative staff cannot enter or advise in situations where livestock or experimental animals are kept in unsanitary conditions. These conditions not only jeopardize the living environment of nearby residents but also lead to situations where animals are subjected to abuse or neglect, resulting in their weakening.
2.Mandate reporting by animal keepers in case of accidents involving humans.
Reason: Currently, ordinances require keepers to report human accidents, mostly limited to dogs and specific animals except for four prefectures that include all animals. To grasp the situation and trends of accidents, it should be mandatory by law.
3.Remove the special clause for the 8-week age restriction for the 6 types of Japanese dogs.
Translated By: Seika.K
Reason: This is an issue left unresolved from the last revision. There is no valid reason to continue this exception, and it should be removed.